The Glasgow Breakthroughs: Fuel cells

On November 2nd, the COP26 launched the Glasgow Breakthroughs, a set of goals to help countries collectively meet the Paris Agreement commitments. For the latter, 42 world leaders agreed to pursue efforts to limit global warming to 1,5°C by halving global emissions by 2030.
The Glasgow Breakthroughs aim to accelerate clean technology development and make such solutions more accessible to more companies, particularly in the most carbon-intensive industries. Five key economic sectors were identified as priorities: Power, road transport, steel, agriculture, and hydrogen.
The production of green hydrogen, a carbon-free fuel created by using electricity in water to split hydrogen molecules from oxygen, spent decades under research as a sustainable fuel alternative. Its use of batteries and power generators—and their components, fuel cells—could impact sectors like transportation and shipping, but also industrial ecosystems and the global energy market.
Let’s dive deeper into fuel cells.
L'Atelier’s Technology Intelligence Engine suggests Europe leads in terms of grants and investments in fuel cell R&D. This is not just through the European Commission’s budget (see “Belgium” data below): Germany, the United Kingdom and Denmark have all put money on fuel cells.
50 percent of Danish electricity is supplied by wind and solar power. No surprise, then, that Denmark has been dreaming big: It is working on creating the biggest fuel cell factory in the world, and the largest hydrogen plants.
The United States looks more like a follower than a challenger in this market. China leads research, topping publications and patents data. But it’s not limiting itself, either. In January 2021, Hyundai Motor Group announced plans to build a fuel cell production plant in Guangdong Province. Three months later, Beijing announced that, by 2025, it would put 10.000 fuel cell vehicles on the road and build 74 hydrogen filling stations.
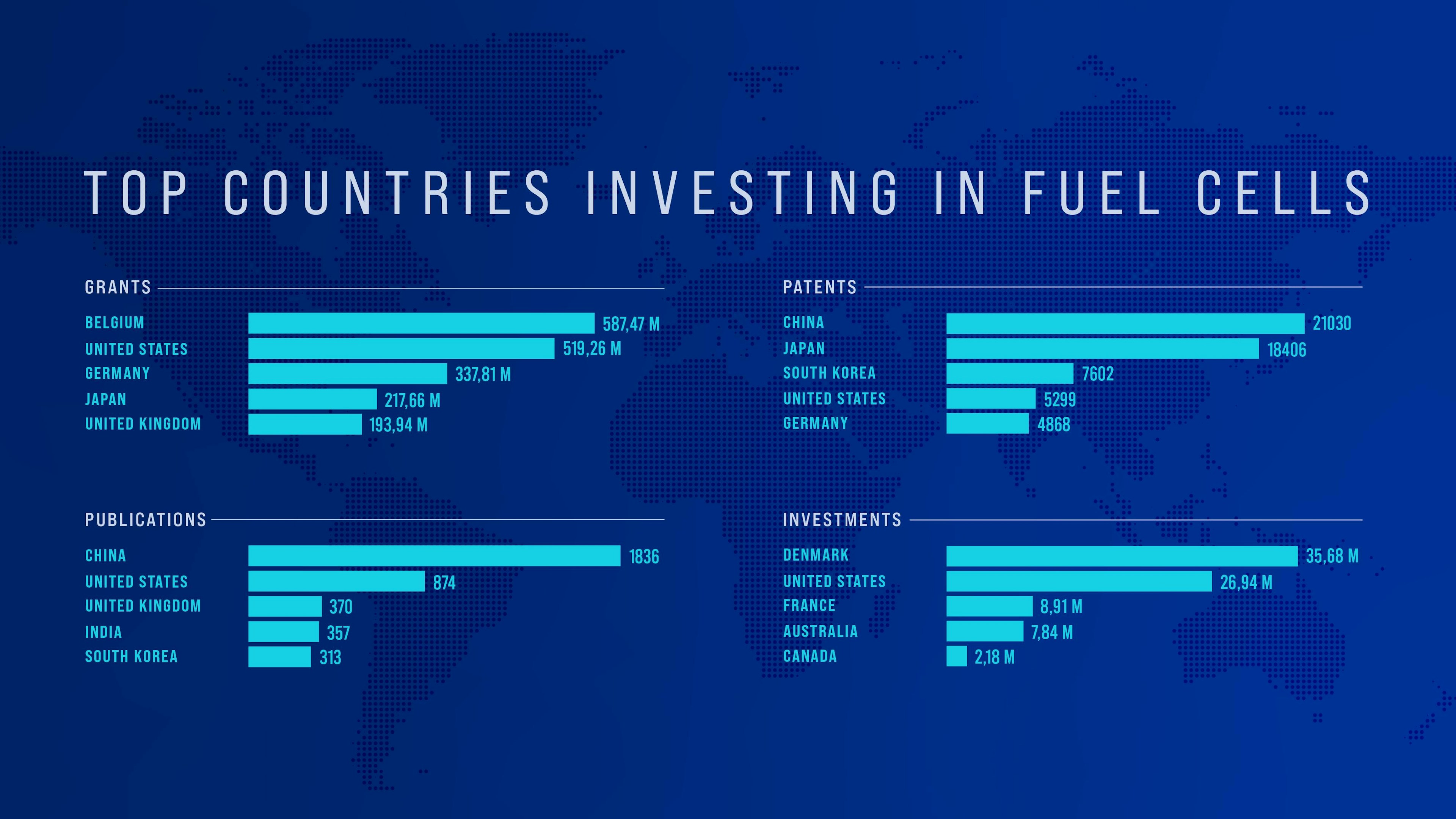
Fuel cell R&D investments (world). Source: the L'Atelier Technology Intelligence Engine.
Who invests where
Almost all the organisations that received fuel cell grants or investments are in the automotive or aerospace industries. But over the past five years, the European Commission massively invested in Element Energy, a consultancy specialised in zero-carbon projects. Last summer, the Cambridge-based company joined a global sustainability consultancy ERM, so expect them to strengthen their leadership.
One surprising startup is Bioo. While investments and grants have mostly been allocated to developing fuel cells for transport and mobility, Bioo is focused on precision agriculture. It’s working on sustainable sensors to monitor crops, powered by microbial fuel cells—meaning that the electricity used to power the sensor is created by organic matter and fertilisers.

Top fuel cell grants & investments (Europe). Source: The L'Atelier Technology Intelligence Engine.
Like Europe, China has mainly focused its hydrogen fuel cell development on automotive and aerospace. What’s striking is that two main grants are going to Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Qualitative research shows that its aim is to find even cleaner alternatives to hydrogen extraction.
Last summer, Hong Kong Polytechnic revealed it created the first ammonia-powered fuel cells.
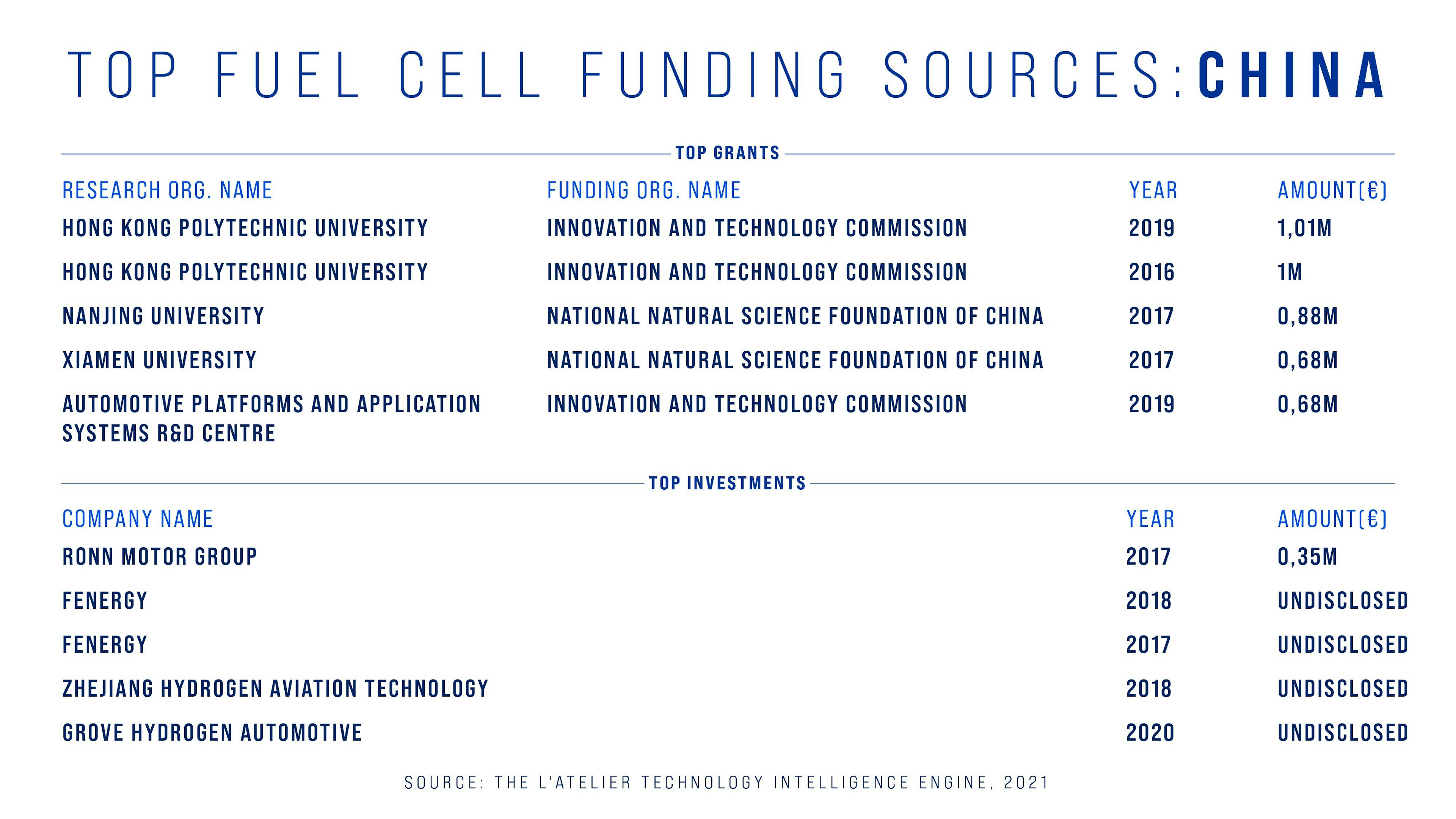
Top fuel cell grants & investments (China). Source: The L'Atelier Technology Intelligence Engine.
Insights
Our engine allows us to monitor global trends in publications, patents, grants and investments over five years. Here’s what we discovered:
- The fuel cell market was particularly impacted by the Covid-19 pandemic, with dramatic drops in patents and investments starting from early 2020. Ironically, fuel cells were leveraged to limit the pandemic’s impact: They were used as a primary energy source to power field hospitals in South Africa. Researchers also say a next step for hydrogen fuel cells could be supplying electricity to locked-down residential areas.
- Research publications on fuel cells, on the other hand, have thrived globally before and since the pandemic’s start. Why? Because it’s not perfect yet. The field has received criticism over the fact that it’s not as sustainable as initially believed. It also doesn't help that Elon Musk has been vocal about dismissing their potential for the automotive industry.
This information comes from the L’Atelier Technology Intelligence Engine, which conducts deep quantitative analysis of large distributed datasets related to technology. To learn more, please reach out. Also, explore larger EU ambitions to drive collective technological change with our State of the EUnion series on blockchain technology and quantum computing.
29 Dec 2021
-
Aurore Geraud
Illustrations by Debarpan Das.
DATA-DRIVEN TECH & SOCIAL TRENDS. DISCOVERED WEEKLY. DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX.
02/03
Related Insights
03/03
L’Atelier is a data intelligence company based in Paris.
We use advanced machine learning and generative AI to identify emerging technologies and analyse their impact on countries, companies, and capital.


